Bearings play a pivotal role in the smooth functioning of industrial machinery. Their primary objective is to regulate motion in moving parts and significantly reduce friction. But did you know there are various types of bearings, each tailored for specific purposes, with unique pros and cons?
Applications of Cylindrical Roller Bearings
 If you have marveled at the efficiency and effectiveness of bearings, you may have already deduced the importance of Cylindrical Roller Bearings. Integral to any machinery with rotating components, they find extensive applications in the following sectors:
If you have marveled at the efficiency and effectiveness of bearings, you may have already deduced the importance of Cylindrical Roller Bearings. Integral to any machinery with rotating components, they find extensive applications in the following sectors:
- Papermaking industry
- Electric motors
- Railways
- Motorcycles
- Pumps
- Wind turbines
- Gearboxes
Their presence in the sectors above speaks volumes about their high performance and durability, even under strenuous conditions. However, thanks to their robust design and resilience, their versatility continues.
What Makes Cylindrical Roller Bearings Different?
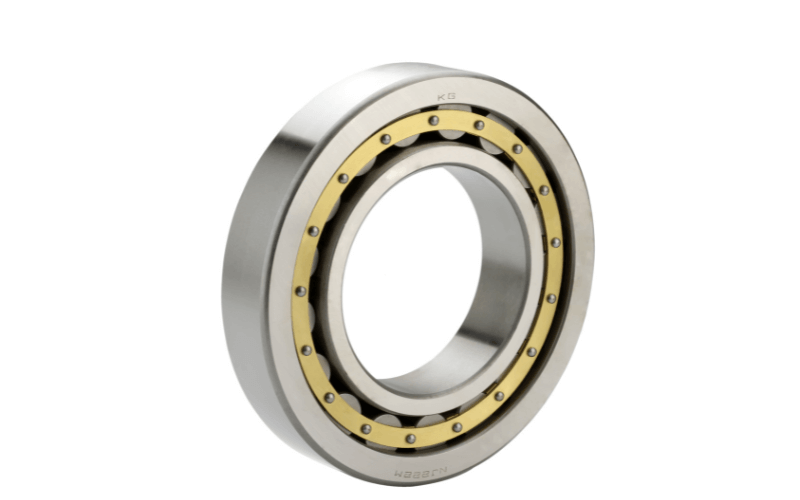
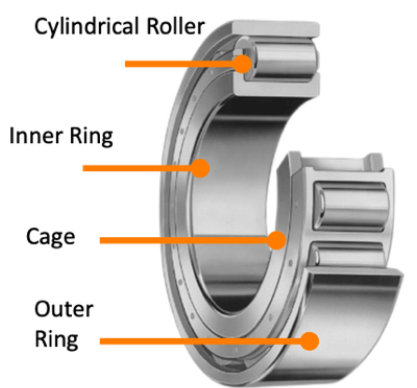
 When diving into the world of bearings, one might wonder about the uniqueness of cylindrical roller bearings. The distinction lies in their use of cylinders. Unlike other bearings, cylindrical rollers boast a superior radial load capacity, surpassing ball bearings. Characterized by cylinders slightly longer than their diameter, they are designed for relatively higher speeds than other roller bearings. Cylindrical Roller Bearings have one of the most straightforward constructions in the roller bearing category. Their design, which ensures a linear contact between the rolling elements and bearing rings, provides a larger contact surface area. This design facet allows them to manage a significantly greater radial load than a Ball Bearing. However, their axial load-bearing capacity is somewhat limited.
When diving into the world of bearings, one might wonder about the uniqueness of cylindrical roller bearings. The distinction lies in their use of cylinders. Unlike other bearings, cylindrical rollers boast a superior radial load capacity, surpassing ball bearings. Characterized by cylinders slightly longer than their diameter, they are designed for relatively higher speeds than other roller bearings. Cylindrical Roller Bearings have one of the most straightforward constructions in the roller bearing category. Their design, which ensures a linear contact between the rolling elements and bearing rings, provides a larger contact surface area. This design facet allows them to manage a significantly greater radial load than a Ball Bearing. However, their axial load-bearing capacity is somewhat limited.
Many variants are tailored to specific application needs, such as NU, NJ, N, NF, NUP, NN, and more. For instance, Double Row Cylindrical Roller Bearings, compared to their single-row counterparts, are preferred for applications demanding higher speed and precision, like in machining centers. Typically paired with Plummer Blocks, these bearings have two bore types: cylindrical and taper. Furthermore, their cages are crafted from pressed steel or polyamide resin, offering flexibility based on the application’s demands.
Why Choose a Cylindrical Roller Bearing?
 Cylindrical roller bearings are a popular choice among many engineers and professionals, and for good reasons. One of the standout features of cylindrical roller bearings is their versatility. Additionally, cylindrical roller bearings can handle some axial load in one direction, especially when the inner or outer rings are designed with two ribs. Double-row cylindrical roller bearings are the go-to-choice for applications requiring high radial rigidity, primarily used in precision machine tools.
Cylindrical roller bearings are a popular choice among many engineers and professionals, and for good reasons. One of the standout features of cylindrical roller bearings is their versatility. Additionally, cylindrical roller bearings can handle some axial load in one direction, especially when the inner or outer rings are designed with two ribs. Double-row cylindrical roller bearings are the go-to-choice for applications requiring high radial rigidity, primarily used in precision machine tools.
While sharing some similarities with radial ball bearings, these bearings have distinct features that set them apart.
Design and Functionality: Cylindrical roller bearings are designed to carry radial loads while minimizing friction. Like radial ball bearings, they can also manage a slight amount of axial loads, depending on the application and the internal design.
Load Capacities: One of the primary advantages of roller bearings over ball bearings is their ability to support higher load capacities. This is especially crucial in applications where heavy loads are a concern.
Contact Area: The contact area is another significant difference between ball and roller bearings. While ball bearings touch the race at a single point, roller bearings have a much larger contact area. This larger area can distribute the load more evenly, reducing stress on the bearing.
How to Choose the Correct Bearing for Your Project or Application?
The correct bearing is crucial for the machinery’s efficient and smooth operation. Here’s a guide to help you make an informed decision:
- Determine the Load Type: Bearings are designed to handle different loads.
- Radial Load: This is perpendicular to the axis and acts at right angles to the shaft.
- Axial (Thrust) Load: This load is parallel to the axis of rotation and acts in the same direction as the shaft. It becomes a consideration when the load aligns similarly to the shaft.
- Purpose of the Bearing: Bearings play a pivotal role in industrial machinery. Their primary function is to regulate motion in moving parts and significantly reduce friction.
- Evaluate Different Types: Many bearings are available in the market, each designed for specific applications. Understand each type’s purpose, advantages, and disadvantages to make an informed choice.
Advantages of Cylindrical Roller Bearings
- Extended bearing life.
- It can support substantial radial loads.
- Robust and durable.
Disadvantages
- Limited tolerance for high axial loads.
Cylindrical roller bearings are like radial ball bearings in that they are designed to carry a radial load while minimizing friction. Cylindrical roller and radial ball bearings can also handle a small amount of axial loads depending on the application and internal design of the bearings. Roller bearings generally offer higher load capacities than ball bearings of the same size.
The other significant difference between the two bearings is their contact area. For ball bearings, the contact area is a single point where the roller bearings hit a much larger area.
Read More: Overview of Roller Bearing
KG International – Your One-Stop Bearings Solution:
At KG International, we pride ourselves on being the comprehensive solution partner for all your bearing requirements. Over the years, we’ve assisted distributors and manufacturers worldwide in procuring the bearings and other aftermarket parts they require. #CHOOSEKG for unparalleled quality and service.