In the complex and dynamic world of engineering and manufacturing, ball bearings are quintessential components recognized for their critical roles in minimizing friction and boosting operational efficiency, particularly in environments where machinery is subjected to heavy loads. This blog aims to provide information about the multifaceted world of ball bearings uses, shedding light on their design, functionality, varied types, applications, and indispensable impact on enhancing machinery across multiple industries.
Understanding Ball Bearings
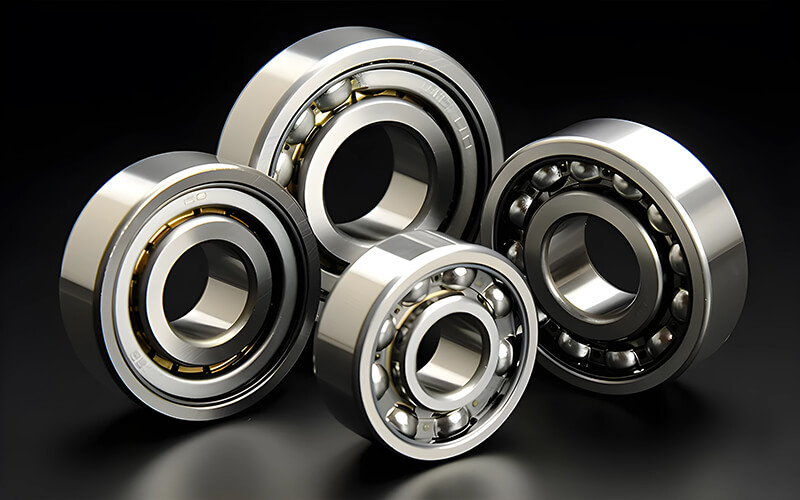
Ball bearings are precisely engineered to manage radial and axial loads, facilitating machine parts’ smooth and efficient rotation. They consist of small but robust balls held securely between two rings, known as the inner and outer rings. The genius of their design lies in the minimal contact area between the load-bearing surfaces, which significantly reduces friction. This design not only allows machine parts to move at higher speeds without overheating but also mitigates wear and tear, substantially extending the lifespan of the machinery.
Purpose of Ball Bearings
The primary purposes of ball bearings are multifaceted and critical to industrial operations:
- Reduction of Friction: Ball bearings enable smoother motion of moving parts while minimizing direct surface contact. This significant reduction in friction helps conserve energy and reduce the operational costs of the machinery.
- Linking Machine Parts: Acting as critical junction points, ball bearings facilitate various machine components’ integration and coherent operation. They ensure that different parts of a machine work together seamlessly.
- Load Bearing: Their robust design makes them essential for bearing substantial radial and axial loads. This capability is particularly crucial in heavy-duty machinery where performance under stress is a constant requirement.
Types of Ball Bearings and Their Applications
There is a wide array of ball bearings, each designed to meet specific functional requirements and load capacities:

Deep Groove Ball Bearings: These are some of the most frequently utilized types of bearings due to their ability to manage radial and moderate axial loads, making them appropriate for various applications.

Angular Contact Ball Bearings: Designed to support higher speed applications, these bearings effectively handle combined loads—supporting both radial and axial forces. They are instrumental in precise applications such as in spindles of machine tools.

Self-Aligning Ball Bearings: These are uniquely designed to cope with shaft misalignments and mounting errors, which are common in many industrial applications. They automatically adjust themselves to align correctly with the machinery.

Thrust Ball Bearings: These are engineered for handling high axial loads at low to moderate speeds and are typically used in applications where radial loads are minimal, like bar stools and turntables.
Ball Bearing Uses Across Industries
The versatility and durability of ball bearings make them integral to numerous sectors:
- Automobile Industry: Ball bearings are critical in various automotive components, including engines, transmissions, and wheel hubs, where they reduce friction, enhance performance, and increase fuel efficiency.
- Manufacturing Industry: Ball bearings are crucial for the seamless functioning of various types of machinery, enhancing the precision and high-speed capabilities required for mass production.
- Robotics Industry: Robotics systems rely heavily on ball bearings for their high precision, efficiency, and ability to handle dynamic loads, crucial for the smooth operation of robotic arms and other moving parts.
- Mechanical and Engineering Applications: Ball bearings find applications in diverse mechanical and engineering contexts, from small household appliances to large industrial equipment like turbines and pumps.
- Commercial Automotive and Transportation: In the transportation sector, ball bearings are critical to the reliable operation of vehicles, from bicycles to large commercial trucks, playing a vital role in safety and performance.
- Medical and Healthcare Applications: In this field, ball bearings are used in various equipment, from hospital beds to high-precision devices such as MRI machines, where reliability and precision are paramount.
The Impact of Ball Bearings on Efficiency and Longevity
The strategic implementation of ball bearings in machinery significantly enhances efficiency and longevity. By efficiently reducing friction, ball bearings decrease the energy required for machines to operate, saving on operational costs, and minimizing heat generation and component wear. This prolongation of machinery life is especially critical in heavy-load environments, where the durability of every component counts.
Ball bearings continue to evolve, with advancements incorporating materials like stainless steel and engineered plastics, which offer excellent durability, corrosion resistance, and suitability for high-speed applications. These innovations are crucial in today’s industries, where reliability and peak performance are essential.
Conclusion
The critical role that ball bearings play in many industrial applications is essential. At KG International, we pride ourselves on specializing in providing top-tier ball bearings that cater to a broad spectrum of industry requirements across the globe. Our commitment to quality and customer satisfaction ensures that each bearing we deliver dramatically improves efficiency and extends the durability of your machinery. With a deep-rooted reputation for reliability and excellence, KG International is your dependable partner in providing robust industrial solutions that meet the highest standards.